How to Stop High Pitched Ringing in Ears: Effective Remedies and Prevention
🧘♀️ Living with a Constant High-Pitched Ring
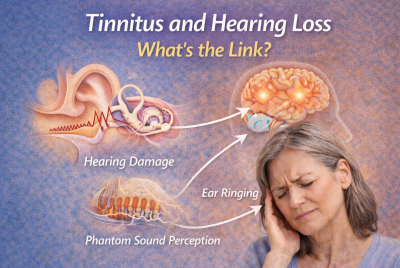
If you’ve ever experienced a high-pitched ear noise, buzzing, or whooshing in your ears that doesn’t seem to go away, you know how frustrating and overwhelming it can be. For millions of Americans, this isn’t just an occasional annoyance—it’s a daily challenge known as tinnitus. The constant ear buzzing sound can affect your sleep, concentration, and even your mental health. The good news? You’re not alone, and there are actionable steps you can take to learn how to stop high pitched ringing in ears. From medical treatments to natural remedies, lifestyle changes, and prevention strategies, this guide will give you practical solutions to manage and reduce your symptoms.
💡 What Causes High-Pitched Ringing in the Ears?
Before learning how to stop the noise, it helps to understand what might be causing it. Tinnitus is not a condition itself but a symptom of an underlying issue.
🧰 Common Causes of High-Pitched Ear Noise
-
Hearing loss – Often age-related or due to prolonged noise exposure.
-
Loud noise exposure – Concerts, headphones, or power tools can lead to tinnitus after loud noise.
-
Earwax blockage – A simple but common trigger of sudden tinnitus.
-
Neck and jaw problems – Known as cervical tinnitus causes, tension or misalignment can worsen symptoms.
-
Medical conditions – High blood pressure, diabetes, or circulatory issues.
-
Medications – Certain antibiotics, cancer drugs, or high doses of aspirin.
🏁 Symptoms Beyond the Ringing
Tinnitus isn’t just “ear ringing.” It can vary in sound, intensity, and duration. Some people experience:
-
Constant ear ringing or intermittent bursts
-
Pulsatile tinnitus (a rhythm matching your heartbeat)
-
Ear ringing at night, making it difficult to sleep
-
Buzzing, clicking, or whooshing in ears
-
Difficulty focusing in quiet environments
🔍 How to Stop High Pitched Ringing in Ears: Medical Options
If your tinnitus is persistent or worsening, a medical evaluation is crucial. Here are some treatments doctors may recommend:
1. Hearing Aids for Tinnitus
For people with hearing loss, hearing aids for tinnitus can amplify external sounds, reducing the contrast with internal ringing.
2. Sound Masking Devices
Special devices or apps create background noise that helps drown out the ringing. Options include:
-
White noise for tinnitus machines
-
Mobile apps offering tinnitus sound therapy
-
Smart earbuds with masking technology
3. Prescription Treatments
-
Antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications (for stress-related tinnitus)
-
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) – retrains the brain’s response to ringing sounds
-
Newer tinnitus retraining therapy programs are available in the U.S.
💊 Natural Remedies and Lifestyle Adjustments
Many people prefer natural tinnitus treatment strategies that can be practiced at home.
1. Stress Management
There’s a strong stress and tinnitus connection. Stress makes the ringing louder and harder to ignore. Techniques include:
-
Yoga or tai chi
-
Meditation and breathing exercises
-
Journaling or progressive muscle relaxation
2. Diet and Supplements
Specific nutrients support hearing health and nerve function:
-
Best supplements for tinnitus may include magnesium, zinc, and B vitamins
-
Omega-3 fatty acids support circulation
-
Reducing caffeine, alcohol, and high-sodium foods may help minimize flare-ups
3. Exercise and Movement
Regular physical activity improves blood flow, which benefits the auditory system. Gentle exercises such as walking, swimming, or stretching can reduce tension-related tinnitus.
4. Ear and Neck Care
Since some cases are linked to cervical tinnitus causes, posture and muscle relaxation matter.
-
Take breaks from screens
-
Use ergonomic seating
-
Try physical therapy for neck and jaw alignment
🔊 Coping Strategies for Daily Life
Living with tinnitus can feel exhausting, but practical tools can make it easier.
-
Sleep hygiene: Use a fan, white noise machine, or calming playlist to ease ear ringing at night.
-
Focus techniques: Work with background music or ambient noise.
-
Support groups: Many U.S.-based tinnitus support networks offer resources and emotional support.
-
Professional counseling: Helps address frustration and anxiety related to chronic tinnitus.
🏥 Tinnitus Prevention Tips: Protecting Your Hearing
While some tinnitus causes can’t be fully avoided, taking steps to protect your ears greatly reduces your risk of developing high-pitched ear noise or worsening existing symptoms. Prevention is especially important in the U.S., where nearly 15% of adults report some form of tinnitus.
1. Limit Exposure to Loud Sounds
-
Follow the 60/60 rule when using earbuds: keep volume under 60% and limit listening to 60 minutes at a time.
-
At concerts or sporting events, avoid standing near speakers or loud sections of the crowd.
2. Always Use Hearing Protection
-
Earplugs (foam or musician-grade) are affordable and effective at blocking harmful decibels.
-
Noise-canceling headphones are useful for commuters, air travelers, or workers in noisy environments, helping you avoid turning the volume up too high.
3. Manage Ear Health
-
Get regular ear exams to prevent issues like earwax blockages that can trigger or worsen tinnitus.
-
Avoid inserting cotton swabs deep into the ear canal, which can push wax further in.
4. Keep Your Cardiovascular System Healthy
-
High blood pressure and poor circulation can contribute to tinnitus.
-
Eat a balanced diet rich in vegetables, omega-3 fatty acids, and whole grains.
-
Stay active with at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week, as recommended by the CDC.
5. Reduce Stimulants That Affect the Ears
-
Caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol can increase ear ringing in sensitive individuals. Track your intake and cut back if symptoms worsen.
6. Prioritize Stress Management
-
Since stress amplifies the stress and tinnitus connection, use daily relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or tai chi.
-
Even short daily breaks from screens and work can reduce mental and physical tension.
7. Schedule Regular Hearing Screenings
-
Adults over 50 should get annual hearing checks; younger adults exposed to regular loud environments should also test their hearing every 2–3 years.
-
Early detection of hearing changes helps prevent tinnitus from progressing.
👉 This makes the section more action-oriented with clear bullet points, relatable examples, and U.S. statistics.
🔹 Quick Checklist: Protecting Your Hearing
Do’s
-
✅ Wear earplugs at concerts, sports events, and noisy workplaces
-
✅ Keep headphone volume under 60% and limit listening to under an hour
-
✅ Get regular hearing exams, especially if you’re over 50
-
✅ Stay active with exercise to improve circulation
-
✅ Practice stress relief (deep breathing, yoga, tai chi) daily
Don’ts
-
❌ Blast music in headphones, cars, or speakers
-
❌ Use cotton swabs deep in your ear canal
-
❌ Ignore ear pain, sudden hearing loss, or new ringing sounds
-
❌ Rely on caffeine, alcohol, or nicotine if they trigger ringing
-
❌ Skip annual check-ups if you already notice an ear buzzing sound
⚕️ When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention if:
-
The ringing comes on suddenly
-
You notice hearing loss or dizziness alongside tinnitus
-
It’s in one ear only and getting worse
-
You experience pulsatile tinnitus (a heartbeat-like sound)
-
It interferes with your daily life or sleep
Prompt diagnosis helps rule out serious conditions and ensures you get the right treatment.
❓ FAQs About How to Stop High Pitched Ringing in Ears
1. Is high pitched ear ringing permanent?
Not always. Temporary tinnitus from loud noise, earwax buildup, or stress can improve once the cause is removed. Chronic tinnitus, however, may persist but can be managed through sound therapy, lifestyle adjustments, and professional hearing care.
2. What is the best way to stop high pitched ringing in ears quickly?
The fastest relief often comes from sound masking, such as white noise machines, fans, or background music. These tools help distract the brain from the ringing, making it less noticeable, especially during quiet moments or at bedtime.
3. Can stress make high pitched ringing in ears worse?
Yes. Stress is a major trigger for tinnitus flare-ups. When stress levels rise, the brain becomes more aware of internal sounds. Relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, or tai chi can reduce the stress–tinnitus connection and provide relief.
4. What vitamins help reduce ear ringing?
Some studies suggest B vitamins, magnesium, and zinc may support nerve and hearing health. While not a guaranteed cure, these nutrients may help lessen ringing severity. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting supplements for tinnitus management.
5. How do hearing aids help stop ringing in ears?
Hearing aids amplify external sounds, reducing the contrast between environmental noise and tinnitus. Some models also include built-in sound therapy programs, making them highly effective tools for people experiencing constant ear ringing or age-related hearing loss.
6. Can high pitched ringing in ears be prevented?
Yes. Protecting your hearing is key. Limit headphone volume, wear earplugs in noisy environments, and schedule regular hearing exams. Maintaining heart health, reducing caffeine and nicotine, and managing stress also lowers the risk of tinnitus flare-ups.
7. When should I see a doctor for ear ringing?
Seek medical attention if tinnitus starts suddenly, affects only one ear, is accompanied by hearing loss or dizziness, or includes pulsatile sounds. A doctor can rule out serious causes and recommend effective treatment options for relief.
🌈 Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Tinnitus Journey
Learning how to stop high pitched ringing in ears isn’t about one quick fix—it’s about combining strategies that work for your body and lifestyle. From medical support to natural remedies, stress management, and prevention, there are many ways to regain control. Remember: relief is possible, and you don’t have to suffer in silence.
⚠️ Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a licensed healthcare provider before starting or changing any treatment for tinnitus.

- Ear Ringing After Loud Noise Exposure
- When Neck Tightness Causing Ear Ringing
- Neck Exercises for Tinnitus Relief