Noise Induced Tinnitus Prevention: How To Protect Your Hearing From Loud Sounds Before Ringing Starts
👂 When Loud Sounds Turn Into Long-Term Ringing
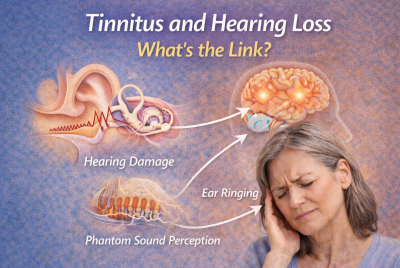
If you’ve ever experienced ringing after a loud concert, construction shift, or music rehearsal, you know how scary it can feel. That high-pitched ringing, buzzing, or whooshing sound can make it hard to sleep, focus, or relax. For some people, the sound fades. For others, it stays.
This is why noise induced tinnitus prevention is so important. Loud sound exposure is one of the most preventable causes of tinnitus in the U.S. Yet millions of people are exposed to dangerous noise levels every day — at concerts, job sites, gyms, or even through headphones.
Understanding how loud noise ear ringing happens — and how to prevent it — can protect your hearing for life.
🔊 What Is Noise Induced Tinnitus Prevention And Why It Matters
Noise induced tinnitus prevention focuses on protecting the inner ear from sound damage before symptoms begin.
Inside your ear are tiny hair cells that help you hear. Loud noise can damage or destroy these cells. Once damaged, they usually do not grow back.
This damage can cause:
-
Constant ringing
-
Buzzing sounds
-
Whooshing noises
-
High-pitched tones
-
Sound sensitivity
Noise exposure is one of the leading causes of tinnitus among younger adults in the U.S., especially with headphone use and live music events.
🔊 How Loud Noise Causes Ear Ringing
❤️ Inner Ear Damage From Loud Sound
When sound is too loud:
-
Hair cells bend or break
-
Nerve signals become irregular
-
The brain creates phantom sound signals
This is why noise induced tinnitus prevention focuses on stopping damage before it starts.
🔊 Common Loud Noise Sources In The U.S.
High-risk exposures include:
-
Concerts and festivals
-
Construction equipment
-
Power tools
-
Firearms
-
Nightclubs
-
Loud fitness classes
-
Personal music players
The concert tinnitus risk is especially high when exposure lasts several hours.
🔊 Noise Induced Tinnitus Symptoms To Watch For
Early warning signs often appear before permanent tinnitus develops.
⚠️ Temporary Warning Signs
-
Ringing after a loud event
-
Ear fullness feeling
-
Sound sensitivity
-
Muffled hearing
-
Head pressure feeling
These symptoms mean your ears were exposed to unsafe sound levels.
🔊 High-Risk Groups Who Need Noise Induced Tinnitus Prevention
🎵 Musicians And DJs
Constant exposure to amplified sound increases tinnitus risk.
🏗️ Construction And Industrial Workers
OSHA requires hearing protection when sound exceeds safe levels, but many workers still experience exposure.
🎧 Frequent Headphone Users
Listening above 60% volume for long periods increases risk.
🎤 Concertgoers And Festival Fans
Repeated exposure increases cumulative hearing damage.
🌿 Noise Induced Tinnitus Prevention Strategies That Work
🌿 Use Hearing Protection Tinnitus Prevention Tools
Modern protection options include:
-
Foam earplugs
-
High-fidelity musician earplugs
-
Noise-reducing earmuffs
-
Custom molded ear protection
Hearing protection tinnitus tools can reduce sound without ruining music quality.
✅ Follow The 60/60 Headphone Rule
-
60% max volume
-
60 minutes at a time
This is one of the simplest noise induced tinnitus prevention strategies.
🌟 Take Listening Breaks
Give ears recovery time after loud exposure.
🧘♀️ Lifestyle Habits That Support Ear Recovery
🌿 Nutrition For Ear And Nerve Health
Support inner ear health with:
-
Magnesium
-
Vitamin B12
-
Antioxidant-rich foods
-
Omega-3 fats
Some people also use ginkgo biloba for circulation support.
🧘♀️ Stress Reduction Helps Tinnitus Perception
Stress can make ringing feel louder.
Helpful methods include:
-
Meditation
-
Breathwork
-
Yoga
-
Guided relaxation apps
💊 Sound Therapy For Loud Noise Ear Ringing
If tinnitus begins, sound therapy can help retrain the brain.
Popular U.S. tools:
-
White noise apps
-
Sleep sound machines
-
Tinnitus maskers
-
Hearing aids with sound therapy
🔊 Prevention Tips For Concert Tinnitus Risk
⭐ Before The Event
-
Bring earplugs
-
Choose seats away from speakers
-
Limit alcohol (can increase blood flow and ringing perception)
✅ During The Event
-
Take sound breaks
-
Step outside periodically
-
Avoid standing directly near speakers
🌟 After The Event
-
Rest your ears in a quiet environment
-
Avoid headphones for 24 hours
-
Hydrate well
🩺 When To See A Doctor For Loud Noise Ear Ringing
See an ENT or audiologist if:
-
Ringing lasts more than 48–72 hours
-
You notice hearing loss
-
Ringing occurs in one ear only
-
You experience dizziness
-
Sound sensitivity becomes severe
Early evaluation improves treatment outcomes.
❓ FAQs About Noise Induced Tinnitus Prevention
1. Can noise-induced tinnitus be permanent?
Yes. If hair cells are permanently damaged, tinnitus can become chronic.
2. How loud is too loud for the ears?
Sounds above 85 dB can cause damage with long exposure.
3. Do earplugs really prevent tinnitus?
Yes. Proper hearing protection and tinnitus tools reduce damage risk.
4. Can tinnitus from concerts go away?
Sometimes. Temporary tinnitus often fades within days.
5. Are noise-canceling headphones safer?
They can help reduce the need for high-volume listening.
6. Is tinnitus more common in musicians?
Yes. Long-term exposure increases the risk significantly.
7. Can supplements prevent tinnitus?
They support ear health, but are not guaranteed to prevent it.
💬 Conclusion: Protect Your Hearing Before Tinnitus Starts
Noise-induced tinnitus prevention is one of the most powerful tools you have to protect lifelong hearing.
Focus on:
-
Using hearing protection
-
Managing volume levels
-
Taking sound breaks
-
Supporting ear health with nutrition and stress control
Small habits today can protect your hearing for decades.
⚠️ Medical Disclaimer
This article is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider regarding tinnitus or hearing concerns.

- Sound Therapy Tinnitus Relief
- Can Energy Drinks Cause Tinnitus?
- What Causes Tinnitus Ringing In The Ears?