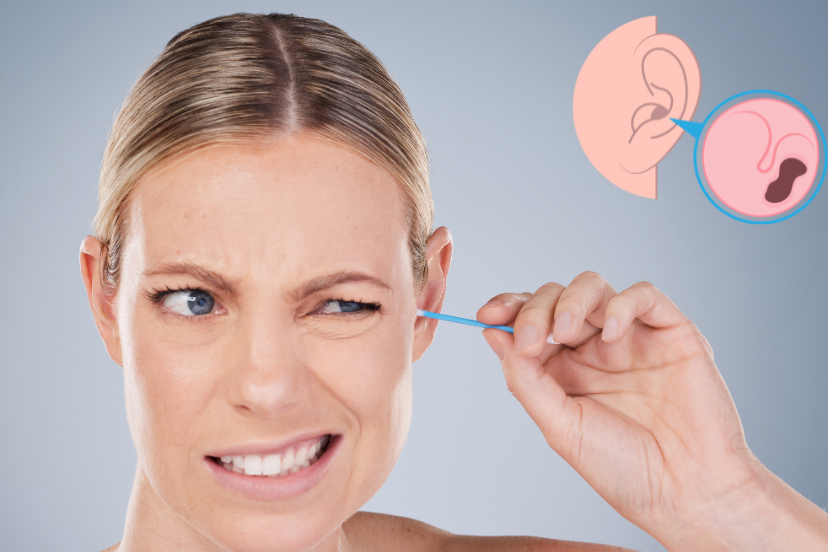
Can Ear Wax Cause Tinnitus
Discover the link between ear wax and tinnitus. Can ear wax cause tinnitus? Unravel the facts and find relief. Dive in to learn more now! I have always been fascinated by the complexities of the human body, particularly when it comes to our hearing. As a researcher and advisor on hearing health, I understand the impact that conditions like tinnitus can have on a person’s quality of life. In this article, I want to address a common question: can ear wax cause tinnitus? Join me as we explore this topic and provide helpful suggestions for managing tinnitus and earwax buildup.
Introduction
Tinnitus is a condition characterized by the perception of ringing, buzzing, or other sounds in the ears without any external source. It can be temporary or chronic, and its impact can vary from mild annoyance to severe disruption. While there are several known causes of tinnitus, the role of earwax often sparks curiosity and concern.
Temporary Vs. Chronic Tinnitus
Temporary tinnitus refers to a temporary perception of ringing or buzzing sounds in the ears that lasts for a short period, often caused by exposure to loud noise or certain medications. On the other hand, chronic tinnitus is persistent and lasts for an extended period, typically more than six months. Chronic tinnitus can be more challenging to treat and may require a comprehensive management approach to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
Understanding Tinnitus
Before diving into the connection between ear wax and tinnitus, let’s briefly understand tinnitus itself. Tinnitus is not a disease but rather a symptom of an underlying issue. It can be caused by various factors, including exposure to loud noise, age-related hearing loss, certain medications, and even stress. While tinnitus can be challenging to treat completely, there are ways to manage its impact on daily life.
Causes Of Tinnitus
Tinnitus can have multiple causes, making it a complex condition. In addition to the factors mentioned earlier, conditions such as ear infections, Meniere’s disease, and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders can also contribute to tinnitus. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for effective management.
The Role Of Ear Wax
Ear wax, also known as cerumen, is a natural substance produced by the ear to protect and lubricate the ear canal. It plays an essential role in preventing dust, debris, and foreign particles from reaching the delicate parts of the ear. However, an excessive buildup of earwax can lead to various issues, including impaired hearing and tinnitus.
Can Ear Wax Cause Tinnitus?
Can Ear Wax Cause Pulsatile Tinnitus?
Ear wax can cause pulsatile tinnitus. Pulsatile tinnitus is a rhythmical noise that often aligns with the heartbeat. When earwax accumulates and blocks the ear canal, it can change the ear’s internal dynamics, potentially leading to pulsatile tinnitus. The wax might alter blood flow or press against blood vessels near the eardrum, causing a pulsing sound. However, many other conditions, like blood vessel disorders or high blood pressure, can also cause pulsatile tinnitus. If you suspect ear wax is the cause, consult a healthcare professional. They can examine your ear and recommend the appropriate treatment. Remember, self-diagnosis or unguided cleaning can worsen the issue.
Can Tinnitus Be Caused By Too Much Ear Wax?
Excessive ear wax can cause tinnitus. When ear wax accumulates, it can block the ear canal, leading to a ringing, buzzing, or humming sound, known as tinnitus. This blockage can interfere with the transmission of sound waves through the ear. Some people notice tinnitus when the buildup becomes significant. However, it’s essential to recognize that many factors can cause tinnitus, and ear wax is just one potential culprit. If someone suspects ear wax is causing their tinnitus, they should consult a healthcare professional. Proper ear wax removal can alleviate the symptoms of those affected by this particular cause. But, using inappropriate methods to clean the ears can worsen the condition or cause further harm, so it’s vital to be cautious.
Symptoms Of Excessive Ear Wax
Recognizing the symptoms of excessive ear wax buildup is important for early intervention. Some common signs include earache, a feeling of fullness in the ear, temporary hearing loss, dizziness, and, in some cases, tinnitus. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s advisable to seek appropriate care and guidance.
Ear Wax Removal Methods
Ear wax removal can be done through various methods. One common method is using over-the-counter ear drops specifically designed to soften and loosen the wax, allowing it to come out of the ear naturally. Another option is to flush the ear with warm water using a bulb syringe or specialized irrigation kit. It’s important to exercise caution and avoid inserting objects into the ear, as this can push the wax deeper or cause damage. Seeking professional help from an audiologist or ENT specialist is recommended for safe and effective earwax removal, especially for persistent or impacted wax. Regular ear hygiene practices can also help manage ear wax buildup.
How Do I Know If I Have Ear Wax Causing Tinnitus?
To determine if ear wax is causing your tinnitus, you should look for sure signs and consult a healthcare professional. Ear wax buildup symptoms include a feeling of fullness in the ear, hearing loss, earache, and ringing or buzzing in the ear (tinnitus). If you experience these symptoms, especially after using cotton swabs or pushing the wax deeper, ear wax might be the culprit. Visual confirmation, however, is crucial. A doctor or audiologist can examine your ear canal with an otoscope to identify any wax buildup. If they find excessive wax, they can safely remove it, which might alleviate your tinnitus. Refraining from self-diagnosing or attempting unguided cleaning is essential, as incorrect methods can exacerbate the issue or cause additional ear damage.
Will My Tinnitus Go Away After Removing Ear Wax?
Ear wax buildup can cause tinnitus in some cases. Removing the ear wax may alleviate tinnitus if the wax is the primary cause. However, tinnitus has various reasons, and ear wax is just one of them. If you experience tinnitus, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional or an audiologist to determine its cause. While removing ear wax can relieve some individuals, it may not guarantee a complete resolution of tinnitus symptoms for everyone. Always approach ear cleaning cautiously, as improper removal techniques can exacerbate the condition or cause additional damage to the ear. Remember, getting a proper diagnosis to address tinnitus effectively is crucial.
The Importance Of Professional Help
Professional assistance is vital, especially when dealing with persistent or impacted ear wax. Audiologists and ENT specialists have the expertise and tools to safely examine the ear and remove excess wax. They can also provide guidance on preventive measures to minimize the risk of ear wax buildup and tinnitus.
Preventing Ear Wax Buildup
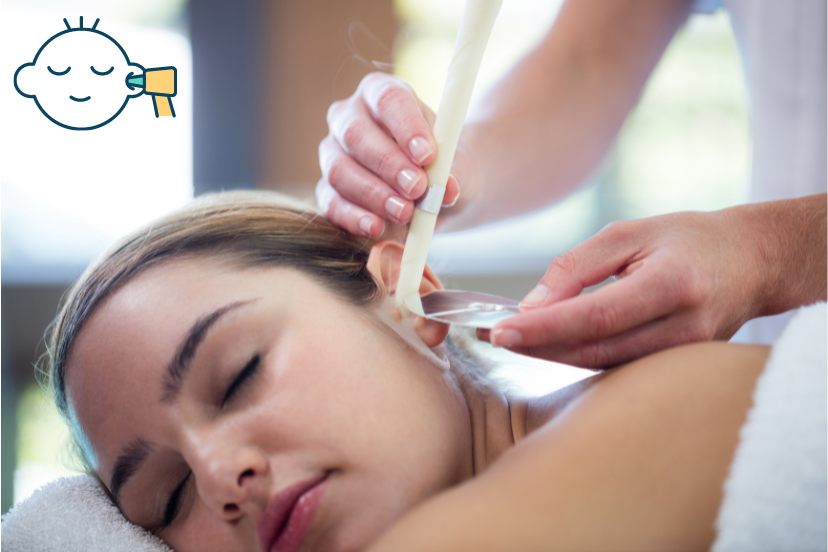
Prevention is always better than cure. By adopting a few simple habits, you can reduce the likelihood of excessive ear wax buildup. Avoid inserting objects like cotton swabs into the ear, as they can push the wax deeper and cause blockages. Additionally, maintaining good ear hygiene and regular check-ups with a healthcare professional can help detect and address any ear-related issues early on.
Tips For Ear Wax Management
Managing ear wax effectively requires a combination of preventive measures and safe cleaning techniques. Some useful tips include using warm water to gently clean the outer ear, using a damp cloth to wipe away excess wax, and using specialized ear drops as recommended by a healthcare professional. Remember, gentle and consistent care is vital.
Tinnitus Management Techniques
While addressing ear wax buildup is important, managing tinnitus requires a holistic approach. Techniques such as sound therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy, stress management, and relaxation exercises can help individuals cope with tinnitus and reduce its impact on daily life. Finding strategies that work best for you and seeking professional guidance if needed is essential.
Seeking Medical Advice
If you or a loved one is experiencing tinnitus, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional. They can conduct a thorough evaluation, determine the underlying cause, and suggest appropriate treatment options. Remember, each case of tinnitus is unique, and personalized advice is essential for effective management.
Addressing Misconceptions
There are numerous misconceptions surrounding tinnitus and its connection to ear wax. It’s important to dispel these myths and rely on accurate information. While earwax can contribute to tinnitus, it’s not the sole cause, and addressing earwax buildup alone may not resolve tinnitus completely. A comprehensive approach is necessary to manage the condition effectively.
Lifestyle Changes For Tinnitus Relief
Specific lifestyle changes can also contribute to tinnitus relief. These include reducing exposure to loud noises, incorporating stress-reducing activities into daily routines, maintaining a healthy diet, and exercising regularly:
Reducing Exposure To Loud Noises
Reducing exposure to loud noises can relieve tinnitus by minimizing further damage to the auditory system. Loud noises can exacerbate tinnitus symptoms and cause additional stress on the delicate structures of the ear. By avoiding loud environments and using ear protection, individuals can reduce the strain on their hearing and alleviate the intensity of tinnitus sounds.
Stress-Reducing Activities
Engaging in stress-reducing activities can help relieve tinnitus by reducing the psychological and emotional impact of the condition. Stress exacerbates tinnitus symptoms, making them more noticeable and bothersome. By practicing activities such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or engaging in hobbies and relaxation techniques, individuals can promote overall well-being and potentially experience a reduction in the intensity and perception of tinnitus.
Healthy Diet
Maintaining a healthy diet can relieve tinnitus by promoting overall wellness and reducing inflammation in the body. Certain foods rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals can support the health of the auditory system and improve blood flow. A balanced diet consisting of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and omega-3 fatty acids may reduce tinnitus symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Regular Exercise
Regular exercise can relieve tinnitus by promoting better blood circulation and reducing stress levels. Exercise helps increase oxygen flow throughout the body, including the auditory system, which can improve overall ear health. Additionally, physical activity releases endorphins, which are natural mood boosters and can help alleviate stress and anxiety associated with tinnitus. Engaging in activities such as walking, swimming, or cycling regularly can reduce tinnitus symptoms.
Though these lifestyle changes may not eliminate tinnitus entirely, they can improve overall well-being and make the condition more manageable.
How Long Does Tinnitus Last After Ear Wax Removal
After removing ear wax, the duration of tinnitus varies among individuals. For some, tinnitus resolves immediately after wax extraction, while others might experience relief within a few hours to several days. If ear wax was the sole cause of tinnitus, symptoms should diminish soon after removal. However, if tinnitus persists for over a week, other underlying causes may be at play. Factors like hearing loss, exposure to loud noises, or certain medical conditions can also trigger tinnitus. If the ringing continues, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional to determine the cause and get appropriate treatment recommendations. Always approach ear care with caution to prevent complications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can tinnitus be cured completely?
Tinnitus is a complex condition, and a complete cure is not always possible. However, various management techniques can help individuals reduce the impact of tinnitus on their daily lives.
2. Are cotton swabs safe for cleaning ears?
Cotton swabs are not recommended for ear cleaning as they can push ear wax deeper and cause blockages. It’s best to avoid inserting any objects into the ear canal and seek professional help for safe wax removal.
3. Can stress worsen tinnitus symptoms?
Yes, stress can worsen tinnitus symptoms. Increased stress levels can amplify the perception of tinnitus sounds, making them more bothersome. It’s important to incorporate stress management techniques into daily routines to help alleviate tinnitus symptoms.
4. Is it normal to have some ear wax?
Yes, it is normal to have a certain amount of ear wax. Ear wax is protected by trapping dust, debris, and foreign particles. However, excessive earwax buildup can lead to various issues, including tinnitus.
5. Can I prevent tinnitus by avoiding loud noises?
While avoiding loud noises can reduce the risk of developing tinnitus, it doesn’t guarantee complete prevention. Tinnitus can have multiple causes, so it’s important to take a comprehensive approach to protect your hearing health.
6. Can ear wax cause vertigo?
Excessive ear wax can block the ear canal and potentially cause vertigo, leading to dizziness and a spinning sensation. If you experience vertigo, consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
7. Can tinnitus go away?
Tinnitus can go away, especially if it results from a temporary condition like earwax buildup or short-term exposure to loud noise. However, some cases may persist. Seeking medical advice can help determine the cause and potential treatments.
Can Ear Wax Cause Tinnitus – Conclusion
In conclusion, while ear wax can contribute to tinnitus, it’s not always the sole cause. However, managing earwax buildup is essential for individuals experiencing tinnitus symptoms. Remember to seek professional help for safe and effective earwax removal, adopt preventive measures to minimize earwax accumulation, and explore various techniques for tinnitus management. By taking a comprehensive approach, individuals can find relief and regain control over their hearing health.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult a licensed healthcare provider before beginning new treatments, supplements, or exercise programs for tinnitus or related conditions.






